A psychological mannequin is a basic concept that can be utilized to clarify many alternative phenomena. Supply and demand in economics, natural selection in biology, recursion in pc science, or proof by induction in arithmetic — these fashions are in all places as soon as you already know to search for them.
Simply as understanding provide and demand helps you purpose about economics issues, understanding psychological fashions of studying will make it simpler to consider studying issues.
Sadly, studying isn’t taught as a category by itself — that means most of those psychological fashions are recognized solely to specialists. On this essay, I’d prefer to share the ten which have influenced me probably the most, together with references to dig deeper in case you’d prefer to know extra.
Herbert Simon and Allen Newell launched the examine of drawback fixing with their landmark ebook, Human Drawback Fixing. In it, they argued that individuals remedy issues by looking by an issue house.
An issue house is sort of a maze: you already know the place you are actually, you’d know in case you’ve reached the exit, however you don’t know how you can get there. Alongside the way in which, you’re constrained in your actions by the maze’s partitions.
Drawback areas may also be summary. Fixing a Rubik’s dice, for example, means transferring by a big drawback house of configurations — the scrambled dice is your begin, the dice with every coloration segregated to a single aspect is the exit, and the twists and turns outline the “partitions” of the issue house.
Actual-life issues are usually extra expansive than mazes or Rubik’s cubes — the beginning state, finish state and precise strikes are sometimes not clear-cut. However looking by the house of prospects remains to be characterization of what folks do when fixing unfamiliar issues — that means once they don’t but have a technique or reminiscence that guides them on to the reply.
One implication of this mannequin is that, with out prior information, most issues are actually troublesome to unravel. A Rubik’s dice has over forty-three quintillion configurations — an enormous house to go looking in in case you aren’t intelligent about it. Studying is the method of buying patterns and strategies to chop down on brute-force looking.
Retrieving knowledge strengthens reminiscence greater than seeing one thing for a second time does. Testing information isn’t only a means of measuring what you already know — it actively improves your reminiscence. Actually, testing is likely one of the greatest examine methods researchers have found.
Why is retrieval so useful? A technique to consider it’s that the mind economizes effort by remembering solely these issues which might be more likely to show helpful. When you at all times have a solution at hand, there’s no must encode it in reminiscence. In distinction, the issue related to retrieval is a powerful sign that you want to bear in mind.
Retrieval solely works if there’s something to retrieve. Because of this we want books, academics and courses. When reminiscence fails, we fall again on problem-solving search which, relying on the scale of the issue house, might fail totally to present us an accurate reply. Nonetheless, as soon as we’ve seen the reply, we’ll be taught extra by retrieving it than by repeatedly viewing it.
How a lot you’re in a position to be taught depends upon what you already know. Analysis finds that the quantity of information retained from a textual content depends upon prior knowledge of the topic. This impact may even outweigh basic intelligence in some conditions.
As you be taught new issues, you combine them into what you already know. This integration offers extra hooks so that you can recall that data later. Nonetheless, when you already know little a few subject, you will have fewer hooks to place new data on. This makes the knowledge simpler to neglect. Like a crystal rising from a seed, future studying is far simpler as soon as a basis is established.
This course of has limits, after all, or information would speed up indefinitely. Nonetheless, it’s good to bear in mind as a result of the early phases of studying are sometimes the toughest and can provide a deceptive impression of future issue inside a area.
Few topics are so misunderstood as creativity. We are likely to imbue artistic people with a near-magical aura, however creativity is way more mundane in observe.
In a formidable assessment of great innovations, Matt Ridley argues that innovation results from an evolutionary process. Slightly than springing into the world fully-formed, new invention is actually the random mutation of previous concepts. When these concepts show helpful, they increase to fill a brand new area of interest.
Proof for this view comes from the phenomenon of near-simultaneous improvements. Quite a few instances in historical past, a number of, unconnected folks have developed the identical innovation, which means that these innovations had been one way or the other “close by” within the house of prospects proper earlier than their discovery.
Even in wonderful artwork, the significance of copying has been uncared for. Sure, many revolutions in artwork had been specific rejections of previous traits. However the revolutionaries themselves had been, virtually with out exception, steeped within the custom they rebelled towards. Rebelling towards any conference requires consciousness of that conference.
Switch refers to enhanced talents in a single activity after observe or coaching in a special activity. In analysis on switch, a typical sample reveals up:
- Apply at a activity makes you higher at it.
- Apply at a activity helps with related duties (often ones that overlap in procedures or information).
- Apply at one activity helps little with unrelated duties, even when they appear to require the identical broad talents like “reminiscence,” “important considering” or “intelligence.”
It’s arduous to make precise predictions about switch as a result of they rely on realizing each precisely how the human thoughts works and the construction of all information. Nonetheless, in additional restricted domains, John Anderson has discovered that productions — IF-THEN guidelines that function on information — kind a reasonably good match for the amount of transfer observed in intellectual skills.
Whereas abilities could also be particular, breadth creates generality. For example, studying a phrase in a international language is just useful when utilizing or listening to that phrase. But when you already know many phrases, you’ll be able to say loads of various things.
Equally, realizing one concept might matter little, however mastering many can provide monumental energy. Each further yr of training improves IQ by 1–5 points, partly as a result of the breadth of information taught in class overlaps with that wanted in actual life (and on intelligence checks).
If you wish to be smarter, there are not any shortcuts — you’ll need to be taught rather a lot. However the converse can also be true. Studying rather a lot makes you extra clever than you would possibly predict.
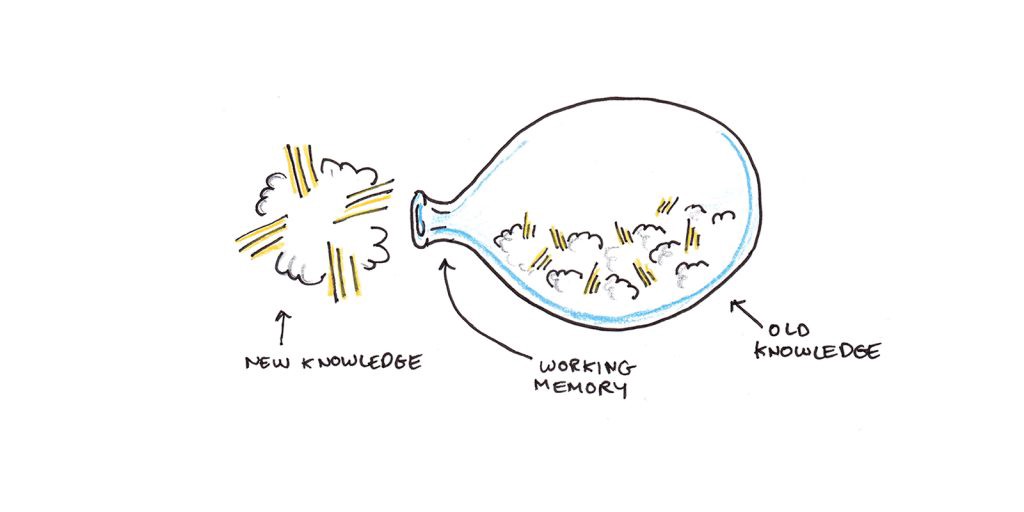
We are able to solely preserve a number of issues in thoughts at anybody time. George Miller initially pegged the quantity at seven, plus or minus two items. However more moderen work has instructed the quantity is closer to four things.
This extremely slim house is the bottleneck by which all studying, each concept, reminiscence and expertise should movement if it will grow to be part of our long-term expertise. Subliminal studying doesn’t work. When you aren’t paying consideration, you’re not studying.
The first means we may be extra environment friendly with studying is to make sure the issues that movement by the bottleneck are helpful. Devoting bandwidth to irrelevant components might sluggish us down.
For the reason that Nineteen Eighties, cognitive load theory has been used to clarify how interventions optimize (or restrict) studying primarily based on our restricted psychological bandwidth. This analysis finds:
- Drawback fixing could also be counterproductive for novices. Novices do higher when proven labored examples (options) as an alternative.
- Supplies needs to be designed to keep away from needing to flip between pages or components of a diagram to grasp the fabric.
- Redundant data impedes studying.
- Advanced concepts may be discovered extra simply when introduced first in components.
We be taught more from success than failure. The reason being that drawback areas are usually massive, and most options are improper. Understanding what works cuts down the probabilities dramatically, whereas experiencing failure solely tells you one particular technique doesn’t work.
A very good rule is to goal for a roughly 85% success rate when studying. You are able to do this by calibrating the issue of your observe (open vs. closed ebook, with vs. with no tutor, easy vs. advanced issues) or by searching for further coaching and help when falling beneath this threshold. When you succeed above this threshold, you’re in all probability not searching for arduous sufficient issues — and are training routines as an alternative of studying new abilities.
How folks can assume logically is an age-old puzzle. Since Kant, we’ve recognized that logic can’t be acquired from expertise. Someway, we should already know the principles of logic, or an illogical thoughts may by no means have invented them. However if this is the case, why will we so usually fail on the sorts of issues logicians invent?
In 1983, Philip Johnson-Laird proposed a solution: we purpose by developing a psychological mannequin of the state of affairs.
To check a syllogism like “All males are mortal. Socrates is a person. Due to this fact, Socrates is mortal,” we think about a set of males, all of whom are mortal, and picture that Socrates is one in all them. We deduce the syllogism is true by this examination.
Johnson-Laird instructed that this mental-model primarily based reasoning additionally explains our logical deficits. We wrestle most with logical statements that require us to look at a number of fashions. The extra fashions that want developing and reviewing, the extra probably we are going to make errors.
Related research by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky reveals that this example-based reasoning can lead us to mistake our fluency in recalling examples for the precise likelihood of an event or sample. For example, we would assume extra phrases match the sample Ok _ _ _ than _ _ Ok _ as a result of it’s simpler to consider examples within the first class (e.g., KITE, KALE, KILL) than the second (e.g., TAKE, BIKE, NUKE).
Reasoning by examples has a number of implications:
- Studying is usually sooner by examples than summary descriptions.
- To be taught a basic sample, we want many examples.
- We should be careful when making broad inferences primarily based on a number of examples. (Are you positive you’ve thought-about all of the attainable circumstances?)
Abilities grow to be more and more automated by observe. This reduces our aware consciousness of the talent, making it require much less of our valuable working reminiscence capability to carry out. Consider driving a automobile: at first, utilizing the blinkers and the brakes was painfully deliberate. After years of driving, you barely give it some thought.
The elevated automation of abilities has drawbacks, nonetheless. One is that it turns into a lot tougher to show a talent to another person. When information turns into tacit, it turns into tougher to make specific how you decide. Specialists ceaselessly underestimate the significance of “fundamental” abilities as a result of, having lengthy been automated, they don’t appear to issue a lot into their every day decision-making.
One other downside is that automated abilities are much less open to aware management. This could result in plateaus in progress if you preserve doing one thing the way in which you’ve at all times achieved it, even when that’s not acceptable. In search of tougher challenges turns into important as a result of these bump you out of automaticity and drive you to strive higher options.
After years spent in class, how many people may nonetheless go the ultimate exams we would have liked to graduate? Confronted with classroom questions, many adults sheepishly admit they recall little.
Forgetting is the unavoidable destiny of any talent we don’t use recurrently. Hermann Ebbinghaus discovered that information tapers off at an exponential rate — most rapidly at first, slowing down as time elapses.
But there’s a silver lining. Relearning is often a lot sooner than preliminary studying. A few of this may be understood as a threshold drawback. Think about reminiscence power ranges between 0 and 100. Beneath some threshold, say 35, a reminiscence is inaccessible. Thus if a reminiscence dropped from 36 to 34 in power, you’ll neglect what you had recognized. However even slightly enhance from relearning would restore the reminiscence sufficient to recollect it. In distinction a brand new reminiscence (beginning at zero) would require way more work.
Connectionist models, impressed by human neural networks, supply one other argument for the efficiency of relearning. In these fashions, a computational neural community might take a whole lot of iterations to succeed in the optimum level. And in case you “jiggle” the connections on this community, it forgets the suitable reply and responds no higher than if by likelihood. Nonetheless, as with the brink rationalization above, the community relearns the optimum response a lot sooner the second time.1
Relearning is a nuisance, particularly since scuffling with beforehand straightforward issues may be discouraging. But it’s no purpose to not be taught deeply and broadly — even forgotten information may be revived a lot sooner than ranging from scratch.
What are the educational challenges you’re dealing with? Are you able to apply one in all these psychological fashions to see it in a brand new gentle? What would the implications be for tackling a talent or topic you discover troublesome? Share your ideas within the feedback!